Exam practice
GCSE Biology: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Biology past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.

GCSE Biology: exam-style questions
CCEA GCSE foundation and higher triple science exam practice with Bitesize interactive quizzes covering feedback and common errors in cells, organisation and more.

GCSE Biology: quick-fire questions
Foundation and higher exam quiz based on CCEA GCSE biology past papers to boost your revision in photosynthesis, respiration, plant disease and more.

Quizzes
QUIZ: Vaccinations and antibiotics
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying treating and preventing diseases - through the provision of vaccinations and antibiotics.

QUIZ: Bacterial growth and drug discovery
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying bacterial growth and how medicines have been developed to fight illness.
QUIZ: Decomposition
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying decomposition and the rate of decay under various circumstances.
Cells
Microscopy, size and magnification
What can we learn about cells and their structure from examining them in very fine detail?
Cells and specialisation
Plants and animals consist of different types of cell that work together. What structures do animal and plant cells have in common?
Diffusion
Diffusion is the random movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.

Living processes
Photosynthesis and plants
Green plants absorb light in their leaves and convert it to energy by photosynthesis.

Nutrition and food tests
Food provides energy and nutrients. Why do the different components of our diet have various sources and functions?

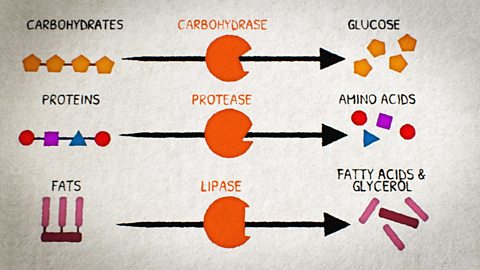
Enzymes and digestion
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, meaning they speed up reactions without being used up.
The respiratory system, breathing and respiration
How is the human respiratory system adapted to allow air to pass in and out of the body, and for efficient gas exchange to happen?

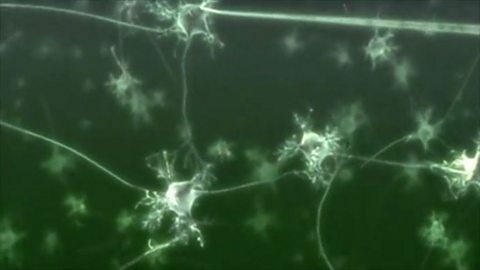
The nervous system
The brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system (CNS). How does the CNS control and coordinate responses between receptors and effectors?
Hormones
Find out how hormones play an important role in maintaining a constant state within the internal environment of the body in response to changes both inside and out.
Biodiversity
Fieldwork and competition
The distribution of organisms in a habitat may be affected by physical factors, such as temperature and light.

Ecological relationships and energy flow
The Sun is the original source of energy for almost all organisms on the Earth. The way energy passes through an ecosystem is described as energy flow.

The carbon cycle and decomposition
Within an ecosystem, why are nutrients (such as carbon or nitrogen) continually recycled?

Global warming, human activity and biodiversity
What are the consequences of global warming and how can its effects be reduced?

The nitrogen cycle, minerals and eutrophication
Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of Earth’s atmosphere and is an essential component in amino acids and proteins.

Body systems
Osmosis and plant transport
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution across a selectively permeable membrane.
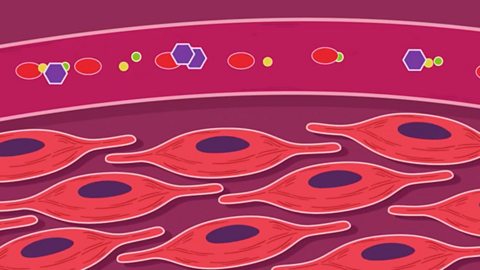
The circulatory system
Blood is pumped away from the heart at high pressure in arteries, and returns to the heart at low pressure in veins.

Reproduction, fertility and contraception
Sexual reproduction involves the joining of two sex cells (gametes) – the sperm (male gamete) and the egg/ovum (female gamete).

Genetics
Chromosones, genes and DNA
Chromosomes are made from DNA. Genes are short sections of DNA. DNA carries genetic code that determines characteristics of a living organism.

Cell division
All cells have a cell cycle, where they grow, copy their DNA, and spilt into new cells during cell division. What are the two types of cell division?
Genetic diagrams and terminology
Genetic diagrams show how characteristics are inherited. Alleles can be recessive, dominant or codominant genes.

X and Y chromosones and genetic screening
Sex is controlled in humans by the X and Y chromosomes. Genetic screening involves testing people for the presence of genetic abnormality.

Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering is a process that modifies the genome of an organism to introduce desirable characteristics.

Variation and natural selection
Organisms of the same species vary in many ways. There are two types – continuous and discontinuous. Natural selection explains how evolution occurs.

Health, diseases and micro-organisms
Communicable diseases
A communicable disease (usually caused by a microorganism such as bacteria, virus or fungus) can be passed from one organism to another.
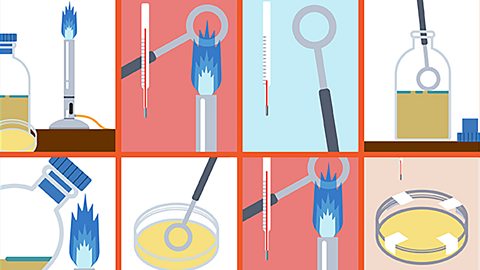
Aseptic techniques
Aseptic techniques are used when working with bacteria and fungi.
Defence mechanisms
The body has adapted defence mechanisms to protect itself against the entry of microorganisms.
Non-communicable diseases
A non-communicable disease is not passed from one organism to another. They are not infectious.

Practical skills
Planning an investigation
Before planning an investigation you need to identify the variables.

Carrying out an experiment
It is essential to learn the relevant practical skills in order to carry out experiments.

Analysing experimental data
Find out how you can analyse, interpret and critically evaluate a range of experimental data.

Drawing conclusions from an experiment
A conclusion is a judgement reached at the end of an investigation using data and/or observations gathered.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription